How to Use the bg Command in Linux?
Understanding the bg Command in Linux
The bg command is a simple yet powerful tool in Linux that allows you to resume suspended jobs and run them in the background. This can be particularly useful for multitasking and optimizing your workflow when using the command line.
What is the bg Command?
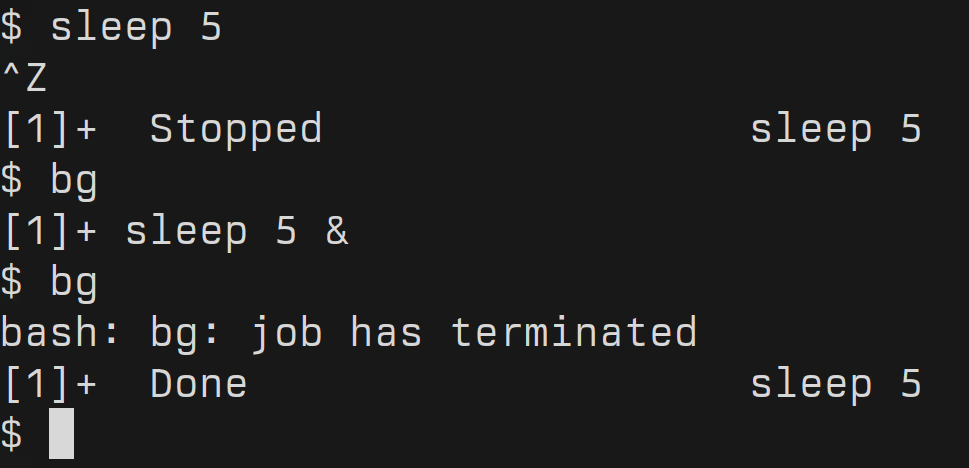
In the Linux environment, when you suspend a job, usually by pressing <Ctrl + Z>, it is placed in a suspended state. The bg command resumes this job and continues its execution in the background. This is particularly helpful when you want to free up your terminal to execute other commands while keeping your previously suspended task running.
How to Use the bg Command
-
Resume the Most Recently Suspended Job: To resume the most recently suspended job and run it in the background, simply type:
bg -
Resume a Specific Job: If you have multiple suspended jobs and want to resume a specific one, first, list all jobs using:
jobs -lThis will display a list of jobs along with their IDs. You can then resume a specific job with:
bg %job_idReplace
job_idwith the actual ID number of the job you wish to resume.
Example Usage
Suppose you have started a long-running process, such as a file transfer or a script execution, and you need to pause it temporarily. You can do so with <Ctrl + Z>. After that, if you decide to check a different task or command, the bg command allows you to resume that paused job in the background.
Conclusion
Utilizing the bg command effectively allows for improved multitasking when using the command line. It keeps your suspended jobs alive and running without clogging your terminal, enabling a more efficient workflow. For further details on the bg command, check the official documentation at manned.org.
Incorporating tools like bg into your command line toolkit can significantly enhance your productivity on Linux.